As I’m building or extending a number of Hyper-V Clusters in the next 4 months I’m gathering/updating my list with the Windows 2008 R2 SP1 hotfixes relating to Hyper-V and Failover Clustering. Microsoft has once published KB2545685: Recommended hotfixes and updates for Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 Failover Clusters but that list is not kept up to date, the two hotfixes mentioned are in the list below. I also intend to update my list for Windows Server 2008 SP2 and Windows 2008 R2 RTM. As I will run into these and it’s nice to have a quick reference list.
I’ll include my current list below. Some of these fixes are purely related to Hyper-V, some to a combination of hyper-V and clusters, some only to clustering and some to Windows in general. But they are all ones that will bite you when running Hyper-V (in a failover cluster or stand-alone). Now for the fun part with some hotfixes, I’ll address in this blog post. Confusion! Take a look at the purple text and the green text hotfixes and the discussion below. Are there any others like this I don’t know about?
* KB2496089 is included in SP1 according to “Updates in Win7 and WS08R2 SP1.xls” that can be downloaded here (http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displaylang=en&id=269) but the Dutch language KB article states it applies to W2K8R2SP1 http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2496089/nl
Artikel ID: 2498472 – Laatste beoordeling: dinsdag 10 februari 2011 – Wijziging: 1.0
Vereisten
Deze hotfix moet worden uitgevoerd een van de volgende besturings systemen:
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Servicepack 1 (SP1) voor Windows Server 2008 R2
Voor alle ondersteunde x64 versies van Windows Server 2008 R2
6.1.7600.20881
4,507,648
15-Jan-2011
04: 10
x64
Vmms.exe
6.1.7601.21642
4,626,944
15-Jan-2011
04: 05
x64
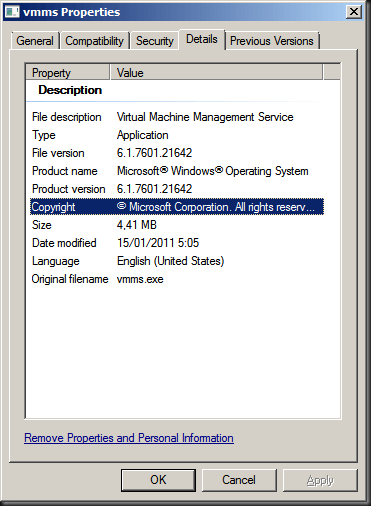
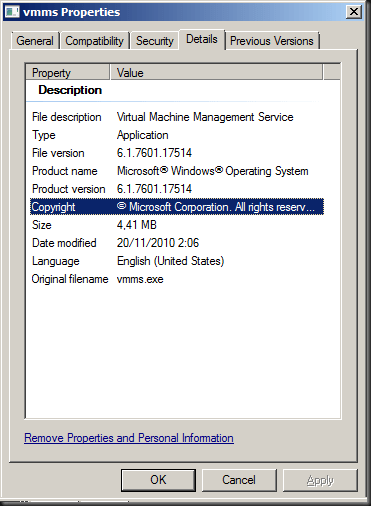
When you try to install the hotfix it will. So is it really in there? Compare file versions! Well the version after installing the hotfix on a W2K8R2 SP1 Hyper-V server the version of vmms.exe was 6.1.7601.21642 and on a Hyper-V server with SP1 its was 6.1.7061.17514. Buy the way these are English versions of the OS, no language packs installed.
With hotfix installed on SP1
Without hotfix installed on SP1
To make matters even more confusing while the Dutch KB article states it applies to both W2K8R2 RTM and W2K8R2SP1 but the English version of the article has been modified and only mentions W2K8R2 RTM anymore.
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2496089/en-us
Article ID: 2496089 – Last Review: February 23, 2011 – Revision: 2.0
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows Server 2008 R2
Vmms.exe
6.1.7600.20881
4,507,648
15-Jan-2011
04:10
x64
So what gives? Has SP1 for W2K8R2 been updated with the fix included and did the SP1 version I installed (official one right after it went RTM) in the lab not yet include it? Do the service packs differ with language, i.e. only the English one got updated?. Sigh :-/ Now for the good news: ** It’s all very academic because of this KB 2521348 A virtual machine online backup fails in Windows Server 2008 R2 when the SAN policy is set to “Offline All” which brings the vmms.exe version to 6.1.7601.21686 and this hot fix supersedes KB2496089. See http://blogs.technet.com/b/yongrhee/archive/2011/05/22/list-of-hyper-v-windows-server-2008-r2-sp1-hotfixes.aspx where this is explicitly mentioned.
Ramazan Can mentions hotfix 2496089 and whether it is included in SP1 in the comments on his blog post http://ramazancan.wordpress.com/2011/06/14/post-sp1-hotfixes-for-windows-2008-r2-sp1-with-failover-clustering-and-hyper-v/ but I’m not very convinced it is indeed included. The machines I tested on are running W2K8R2 English RTM updated to SP1, not installations for the media including SP1 so perhaps there could also be a difference. It also should not matter that if you install SP1 before adding the Hyper-V role, so that can’t be the cause.
Anyway, keep your systems up to date and running smoothly, but treat your Hyper-V clusters with all due care and attention.
- KB2277904: You cannot access an MPIO-controlled storage device in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1) after you send the “IOCTL_MPIO_PASS_THROUGH_PATH_DIRECT” control code that has an invalid MPIO path ID
- KB2519736: Stop error message in Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 or in Windows 7 SP1: “STOP: 0x0000007F”
- KB2496089: The Hyper-V Virtual Machine Management service stops responding intermittently when the service is stopped in Windows Server 2008 R2
- KB2485986: An update is available for Hyper-V Best Practices Analyzer for Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1)
- KB2494162: The Cluster service stops unexpectedly on a Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1) failover cluster node when you perform multiple backup operations in parallel on a cluster shared volume
- KB2496089: The Hyper-V Virtual Machine Management service stops responding intermittently when the service is stopped in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1)*
- KB2521348: A virtual machine online backup fails in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1) when the SAN policy is set to “Offline All”**
- KB2531907: Validate SCSI Device Vital Product Data (VPD) test fails after you install Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
- KB2462576: The NFS share cannot be brought online in Windows Server 2008 R2 when you try to create the NFS share as a cluster resource on a third-party storage disk
- KB2501763: Read-only pass-through disk after you add the disk to a highly available VM in a Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 failover cluster
- KB2520235: “0x0000009E” Stop error when you add an extra storage disk to a failover cluster in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1)
- KB2460971: MPIO failover fails on a computer that is running Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1)
- KB2511962: “0x000000D1” Stop error occurs in the Mpio.sys driver in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1)
- KB2494036: A hotfix is available to let you configure a cluster node that does not have quorum votes in Windows Server 2008 and in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1)
- KB2519946: Timeout Detection and Recovery (TDR) randomly occurs in a virtual machine that uses the RemoteFX feature in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1)
- KB2512715: Validate Operating System Installation Option test may identify Windows Server 2008 R2 Server Core installation type incorrectly in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1)
- KB2523676: GPU is not accessed leads to some VMs that use the RemoteFX feature to not start in Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
- KB2533362: Hyper-V settings hang after installing RemoteFX on Windows 2008 R2 SP1
- KB2529956: Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1) installation may hang if more than 64 logical processors are active
- KB2545227: Event ID 10 is logged in the Application log after you install Service Pack 1 for Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- KB2517329: Performance decreases in Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1) when the Hyper-V role is installed on a computer that uses Intel Westmere or Sandy Bridge processors
- KB2532917: Hyper-V Virtual Machines Exhibit Slow Startup and Shutdown
- KB2494016: Stop error 0x0000007a occurs on a virtual machine that is running on a Windows Server 2008 R2-based failover cluster with a cluster shared volume, and the state of the CSV is switched to redirected access
- KB2263829: The network connection of a running Hyper-V virtual machine may be lost under heavy outgoing network traffic on a computer that is running Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
- KB2406705: Some I/O requests to a storage device fail on a fault-tolerant system that is running Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 (SP1) when you perform a surprise removal of one path to the storage device
- KB2522766: The MPIO driver fails over all paths incorrectly when a transient single failure occurs in Windows Server 2008 or in Windows Server 2008 R2