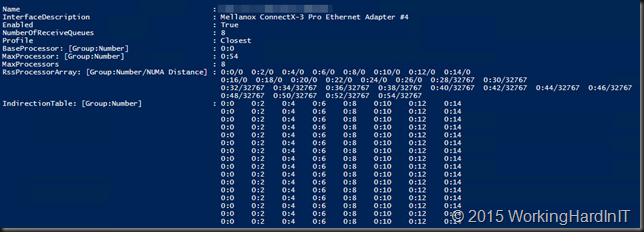
When you have been reading up on what’s new in Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V networking you probably read about Switch Embedded Teaming (SET). Basically this takes the concept of teaming and has this done by the vSwitch. Which means you don’t have to team at the host level. The big benefit that this opens up is the RDMA can be leveraged on vNICs. With host based teaming the RDMA capabilities of your NICs are no longer exposed, i.e. you can’t leverage RDMA. Now this has become possible and that’s pretty big.
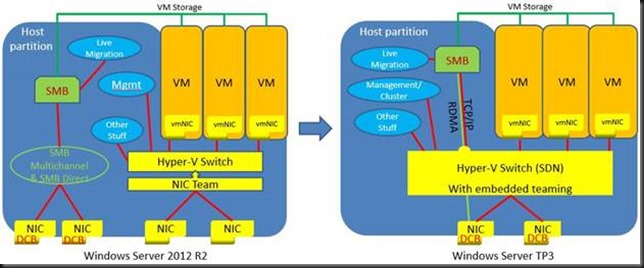
With the rise of 10, 25, 40, 50 and 100 Gbps NICs and switches the lure to go fully converged becomes even louder. Given the fact that we now don’t lose RDMA capabilities to the vNICs exposed to the host that call sounds only louder to many. But wait, there’s even more to lure us to a fully converged solution, the fact that we now do no longer lose RSS on those vNICs! All good news.
I have written an entire whitepaper on convergence and it benefits, drawback, risks & rewards. I will not repeat all that here. One point I need to make that lossless traffic and QoS are paramount to the success of fully converged networking. After all we don’t want lossy storage traffic and we need to assure adequate bandwidth for all our types of traffic. For now, in Technical Preview 3 we have support for Software Defined Networking (SDN) QoS.
What does that mean in regards to what we already use today? There is no support for native QoS and vSwitch QoS in Windows Server 2016 TPv3. There is however the mention of DCB (PFC/ETS ), which is hardware QoS in the TechNet docs on Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) and Switch Embedded Teaming (SET). Cool!
But wait a minute. When we look at all kinds of traffic in a converged Hyper-V environment we see CSV (storage traffic), live migration (all variations), backups over SMB3 all potentially leveraging SMB Direct. Due to the features and capabilities in SMB3 I like that. Don’t get me wrong about that. But it also worries me a bit when it comes to handling QoS on the hardware side of things.
In DCB Priority Flow Control (PFC) is the lossless part, Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS) is the minimum bandwidth QoS part. But how do we leverage ETS when all types of traffic use SMB Direct. On the host it all gets tagged with the same priority. ETS works by tagging different priorities to different workloads and assuring minimal bandwidths out of a total of 100% without reserving it for a workload if it doesn’t need it. Here’s a blog post on ETS with a demo video DCB ETS Demo with SMB Direct over RoCE (RDMA .
Does this mean a SDN QoS only approach to deal with the various type of SMB Direct traffic or do they have some aces up their sleeves?
This isn’t a new “concern” I have but with SET and the sustained push for convergence it does has the potential to become an issue. We already have the SMB bandwidth limitation feature for live migration. That what is used to prevent LM starving CSV traffic when needed. See Preventing Live Migration Over SMB Starving CSV Traffic in Windows Server 2012 R2 with Set-SmbBandwidthLimit.
Now in real life I have rarely, if ever, seen a hard need for this. But it’s there to make sure you have something when needed. It hasn’t caused me issues yet, but I’m a performance & scale first, in “a non-economies of scale” world compared to hosters. As such convergence is a tool I use with moderation. My testing when traffic competes without ETS is that they all get part of the cake but not super predictable/ consistent. SMB bandwidth limitation is a bit of a “bolted on” solution => you can see the perf counters push down the bandwidth in an epic struggle to contain it, but as said it’s a struggle, not a nice flat line.
Also Set-SmbBandwidthLimit is not a percentage, but hard max bandwidth limit, so when you lose a SET member the math is off and you could be in trouble fast. Perhaps it’s these categories that could or will be used but it doesn’t seem like the most elegant solution/approach. That with ever more traffic leveraging SMB Direct make me ever more curious. Some switches offer up to 4 lossless queues now so perhaps that’s the way to go leveraging more priorities … Interesting stuff! My preferred and easiest QoS tool, get even bigger pipes, is an approach convergence and evolution of network needs keeps pushing over. Anyway, I’ll be very interested to see how this is dealt with. For now I’ll conclude my musings On Switch Embedded Teaming, SMB Direct and QoS in Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V