How Windows Server 2012 R2 backups differ from Windows Server 2012 and earlier
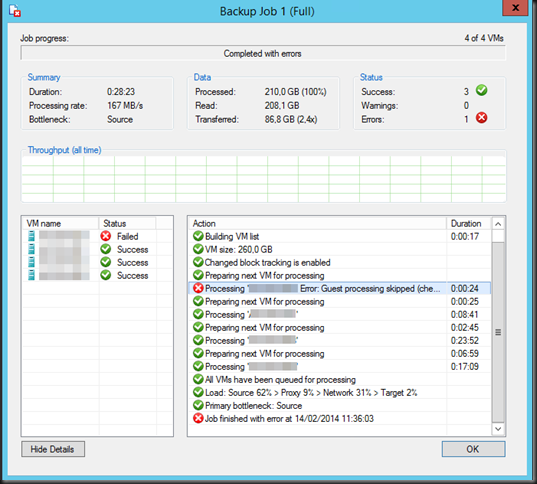
You’ll remember our previous blog about an error when backing up a virtual machine on Windows Server 2012 R2, throwing this error:
Dealing With Event ID 10103 “The virtual machine ‘VM001’ cannot be hot backed up since it has no SCSI controllers attached. Please add one or more SCSI controllers to the virtual machine before performing a backup. (Virtual machine ID DCFE14D3-7E08-845F-9CEE-21E0605817DC)” In Windows Server 2012 R2
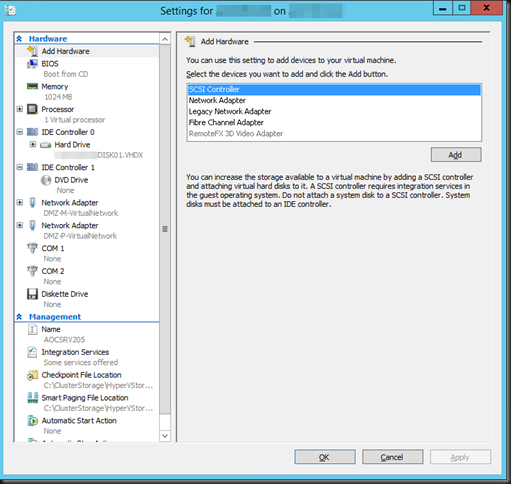
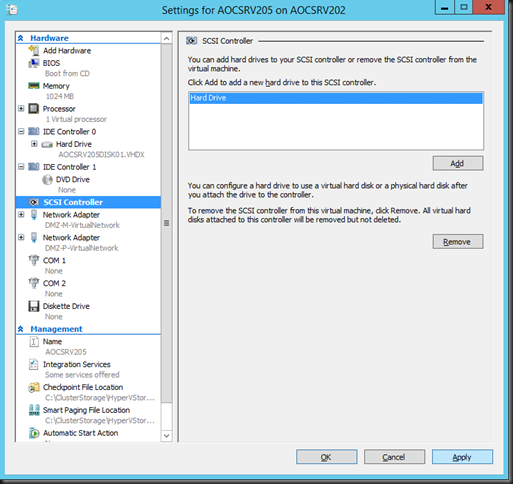
The fix was easy enough, adding a virtual SCSI controller to the virtual machine. But why does it need that now?
Well, this all has to do with the changed way Windows Server 2012 R2 backups work. Before Windows Server 20012 R2 the VSS provider created a VSS snapshot inside the guest virtual machine. That snapshot was exposed to the host, to create a volume snapshot for backup purposes. Right after the volume snapshot has been taken this VSS snapshot inside the guest virtual machine needed to be reverted. The backups then run against that volume snapshot and is consistent thanks to both host & guest VSS capabilities.
For an overview of VSS based backup process in general take a peak at Overview of Processing a Backup Under VSS
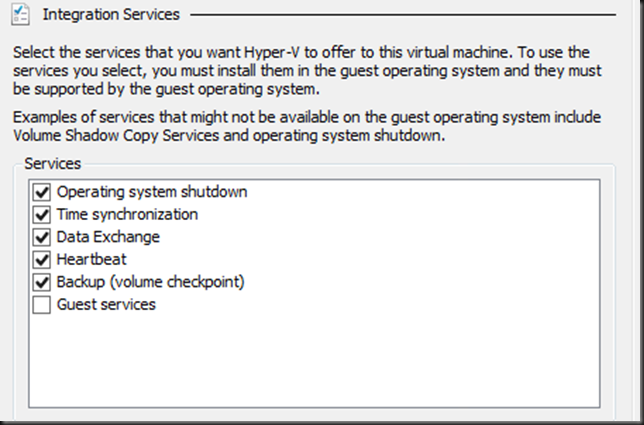
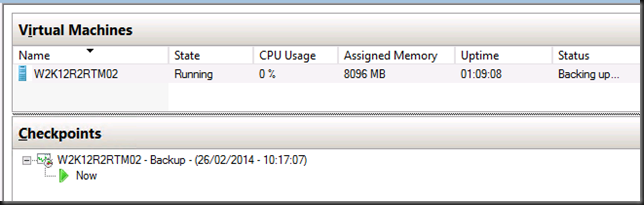
Now it is the “Hyper-V Integration Services Shadow Copy Provider” that is being used. When the the host initiates a volume snapshot (Microsoft or hardware VSS provider) the host VSS writer goes in to freeze. This process leverages the Hyper-V Integration Services Shadow Copy Provider to create the virtual machine checkpoint. After that the volume/LUN/CSV snapshot is taken. When that is done the host VSS writes goes into thaw and the virtual machine checkpoint is deleted. After that the backup runs against the Volume snapshot and at the end that is also deleted. You can follow this process quite nicely in the GUI of your Hyper-V host, you SAN (if you use a Hardware VSS provider).
Dear storage vendors: a great, reliable, fast VSS Hardware Provider is paramount to success in a Microsoft environment. You need to get this absolutely right and out of the door before spending any more time and money on achieving yet more IOPS. Keep scalability in mind when doing this.
Dear backup software vendors: think about the scalability when designing your products. If we have 200 or 500 or a thousand VMs … can we leverage CSV based backups to protect every VM on the LUN or do we need to snap the LUN for every VM backed up? Choice there is good for both data protection schemes and scalability.
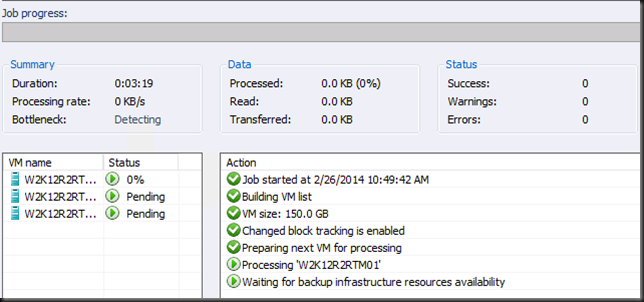
At this stage the hardware VSS snapshot is being taken …
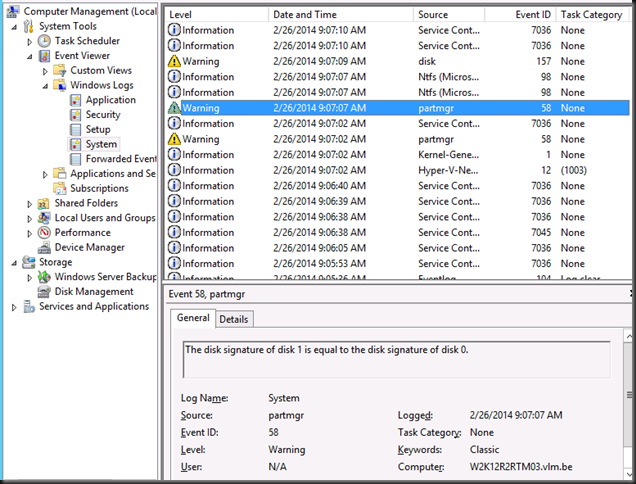
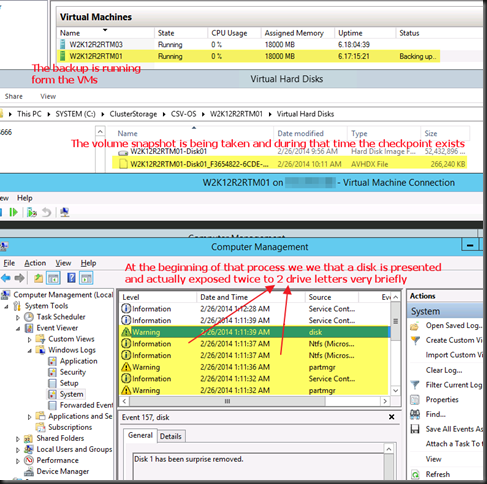
Contrary to common belief this means that the backup will indeed application consistent to the time of the checkpoint as the CSV snapshot being taken is of a consistent checkpoint. It’s the delta in the active avhdx that is only crash consistent, like any running VM by the way. Now pay attention to the screenshot below. The two red arrows are indicating to ntfs source events, two volumes seem to be exposed to the next free drive letters. E: and F: here as C: is the virtual machine OS and D: the DVD.
Look at the detail. Indeed two. Well it the previous screenshot we only saw one in the CSV path but there are two avhdx files indeed.
Exposing a snapshot on the SAN to a server actually shows us this much better … look here at the avhdx with the GUID and one with “AutoRecovery” in the name. So that makes for two nfts events … and as the backup needs to do this life it requires a vSCSI controller to be present in the virtual machine … and vIDE controller can’t do this.
Anyway, enough under the hood detective work for now, In VEEAM that stage looks like this:
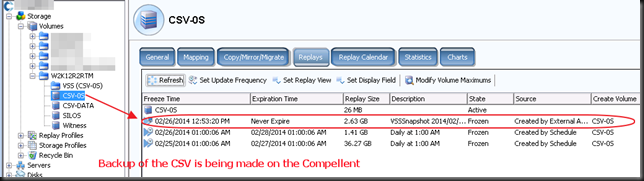
And on the Compellent it looks like this. The screenshots are from different backups at different times so don’t get confused about the time stamps here. It’s just as illustration of what you can expect to see.
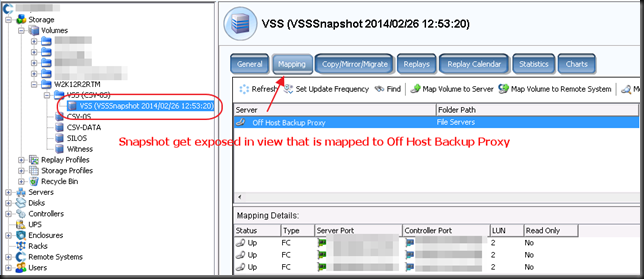
Now when the CSV snapshot has been taken the virtual machine checkpoint is removed. At that time the backup runs against the CSV snapshot. In our case (hardware VSS provider) this is a snapshot on the SAN that gets exposed in a view and mapped to the off host backup proxy VEEAM server. On the DELL Compellent it looks like this.
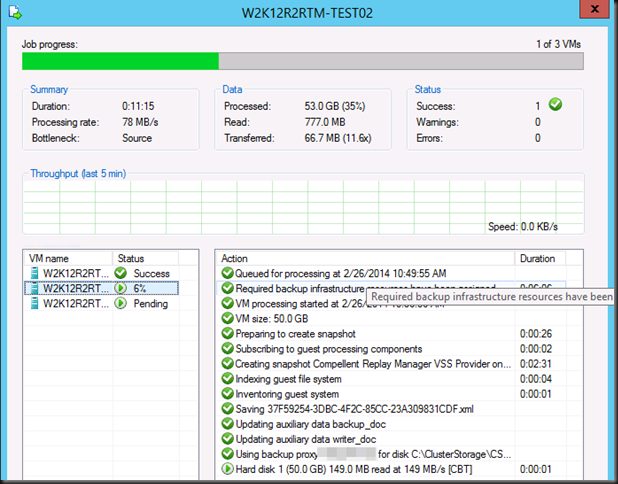
This takes a while to o…but after a while the backup will kick off. Do not that the checkpoint has merged and is no longer visible at this time.
Once the backup is complete, the mapping is removed, the view deleted and the snapshot expired. So your SAN is left as the backup found it.
There you go. I hope this helped clarify certain things on how Hyper-V guest backups work in Windows 2012 R2. So your backups are still application consistent, just not when you’re running Linux or DOS or NT4.0 as there is no support / VSS for that. However they are based on a consistent virtual machine snapshot which explains why Hyper-V backups can protect Linux guests very adequately!

![image_thumb[1] image_thumb[1]](https://blog.workinghardinit.work/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/image_thumb1_thumb.png)
![image_thumb[3] image_thumb[3]](https://blog.workinghardinit.work/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/image_thumb3_thumb1.png)