Introduction
I have discussed the capability of resizing a VHDX on line in this blog post Online Resizing Of Hyper-V Virtual Disks Is Possible in Windows 2012 R2. It’s a good resource to learn how to successfully do so.
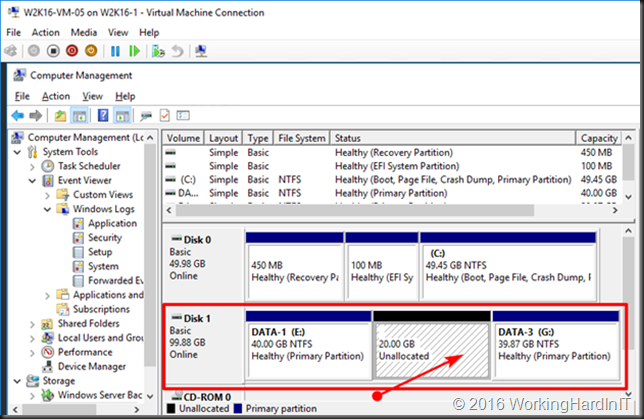
Despite this you still might run into issue. As mentioned in the above blog post you need unallocated disk space at the end of the disk inside the virtual machine or you cannot shrink the VHDX at all. This situation is shown in the screenshot below.
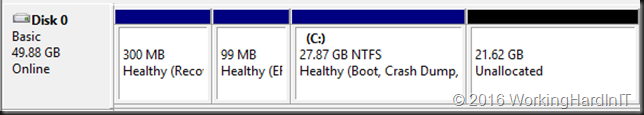
In most cased this will call for you to shrink the volume size inside your virtual machine first as all space might be allocated to the volume. For this article we’ve set up a lab virtual machine to recreate the issue. The virtual machine had the page file disabled initially. We copied lots of data in it and then created shadow copies. Only then did we created a 10GB fixed sized page file to make sure it was somewhere in the beginning of the volume space. All of this was done to simulate a real world situation with lot of data churn over time. We then shift deleted the data. We now take a look at the disk where we need to shrink volume C in order to be able to shrink the virtual disk itself.
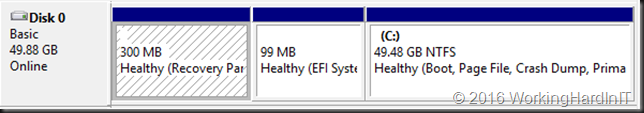
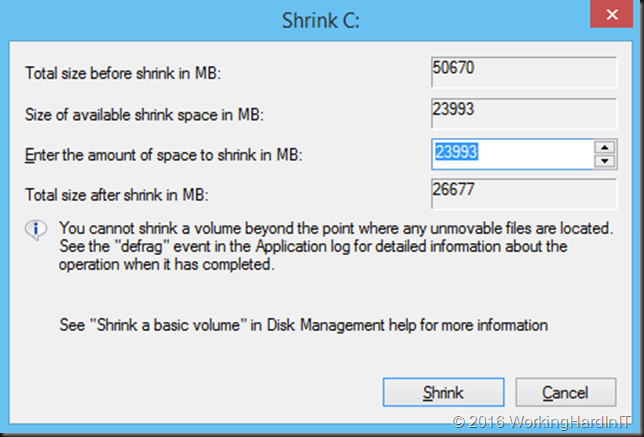
For the shrinking of a volume to succeed you need free space in that volume. But sometimes this doesn’t shrink a virtual machine as much as you’d like or not at all based on the amount of free space you see in the volume as in the figure below.
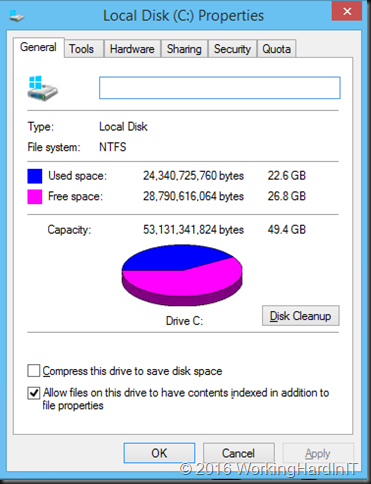
We should be able to free up to 26GB it seems. But when you try to shrink that volume you see this:
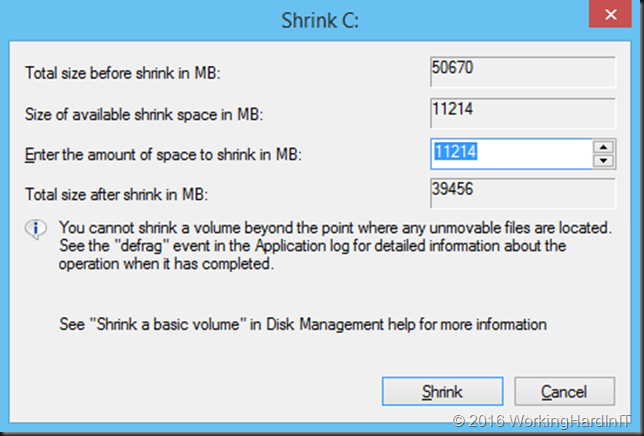
Only 11GB as available shrink space. Not quite what you’d expect based on the free space on the volume! We’ve seen this a couple of times before with virtual servers in real life. The reasons are actually well known, although more often associated with your PC at home than with virtualized servers. So how do we deal with this?
Dealing with a volume with free space that cannot shrink
The issue at hand is most probably that you have files at the end of that volume on your virtual hard disk file that prevent the disk being shrunk. There are a couple tips and tricks associated with getting this fixed.
Defragment the volume
As long as files are movable fragmentation by itself should not prevent resizing a volume. But it never hurts to run it before and it will create continuous free space at the end of the volume that can be shrunk. What’s more important here is that defragmentation cannot move all files, some are unmovable. These files have their fragments scattered all over the place and might prevent you from shrinking the volume.
On modern Windows operating systems defragmentation is part of the storage optimization maintenance job. It also runs UNMAP which informs the virtual hard disk of free space due to data having been deleted.
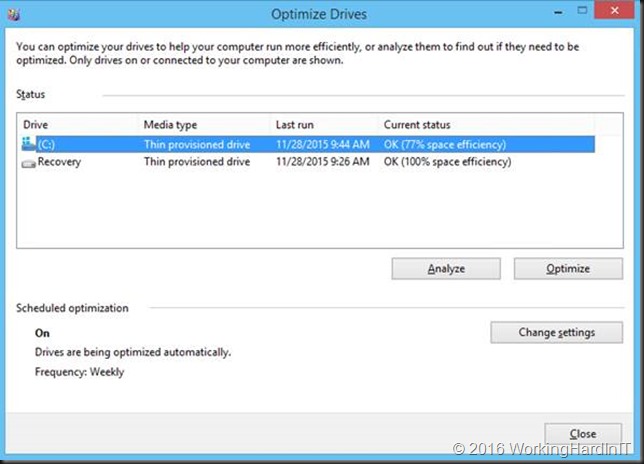
That’s all good and it means that you don’t even need to run defragmentation manually. But how can we deal with these unmovable files?
There are free and commercial tools that can defragment unmovable files during a boot time defragmentation run. They can even defragment and move system files that are otherwise impossible to move. A commercial tool can do off line defragmentation of your page file and other system files. By doing the defragmentation during boot time they can handle NTFS metadata files on the %systemdrive% directory (usually C:\) such as $MFTMirr, $LogFile, $Volume, $Bitmap, $Boot, and $BadClus:$Bad.
Not all unmovable files can be dealt with this way however. You must realize that since Windows vista the contents of the System Volume Information directory where Windows stores System Restore Points (shadow copies) are completely off-limits to defragmentation software.
As with many things there are manual workarounds.
Remove any “previous versions” or restore points created by shadow copies
Space efficient as these shadow copies for data protection are they can and do consume space on the disk you’re trying to shrink. As mention above, we cannot deal with them via defragmentation. Getting rid of them temporarily can help in this case. Just enable them again if needed when you’re done resizing the volume.
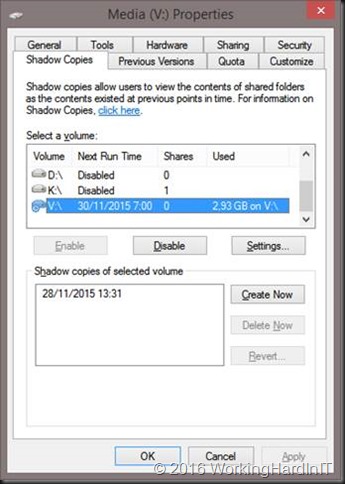
Tip: You can locate the shadow copies to be on a different disk. That’s worth considering when they grow large for both space considerations and performance.
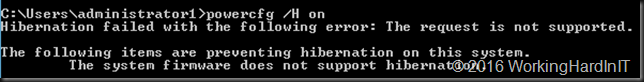
Could the hibernation file cause issues?
We are discussing resizing and virtual hard disk and on virtual machine you won’t find a hyberfil.sys file. This only comes in to play when shrinking a volume on physical hardware. Hibernation is not supported or even available inside a guest OS. You can see this if you try to enable it:
Disable the page file
The page file itself can be come fragmented and it can reside completely or partially on a location of the disk that prevents the volume from being shrunk. While a page file is important to the operating system you can disable it during a maintenance window to make sure it doesn’t block resizing of the virtual hard disk. Be aware that both disabling and re-enabling the page file requires a reboot. So this does mean the online VHDX resize will cause downtime but that’s not because it’s not supported, but because of the action you need to take here to be able to shrink the volume.
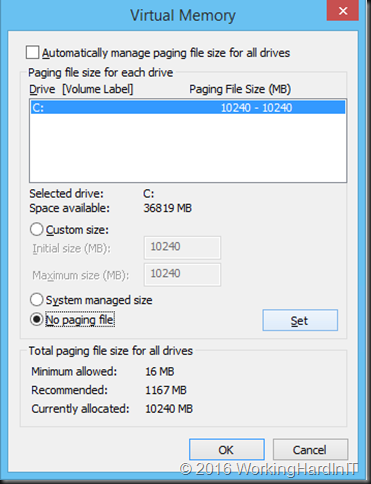
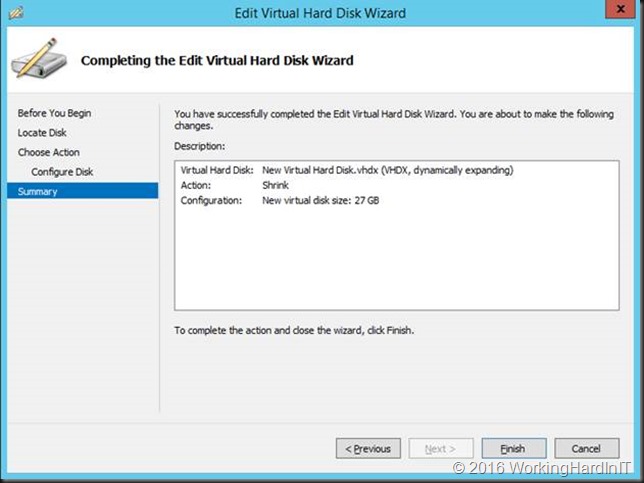
The little extra unallocated space left is taken care or by extending the disk a little. Done!
Don’t forget to turn the page file back on in the best possible configuration for your workload afterwards.
Some situations require even more drastic interventions
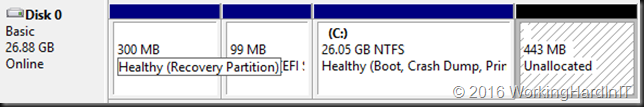
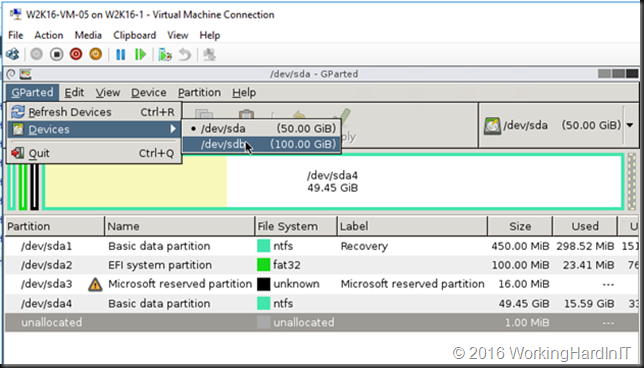
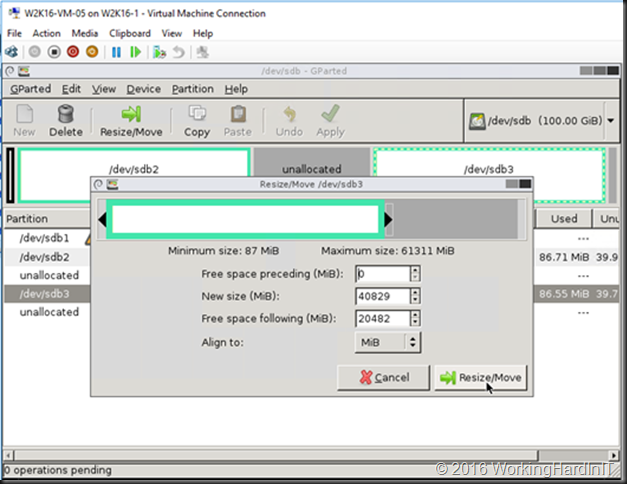
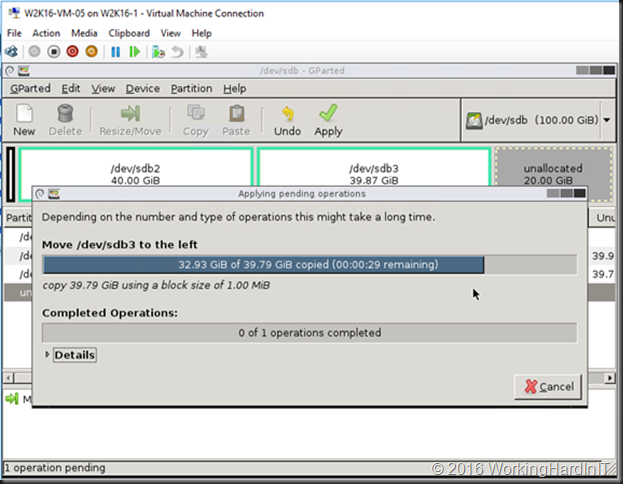
Another issue might be that there are multiple volumes on the virtual hard disk and the free space is not at the end of the disk as in the below screen shot.
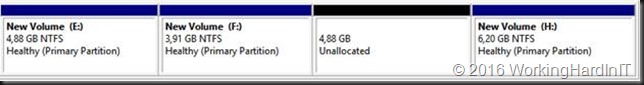
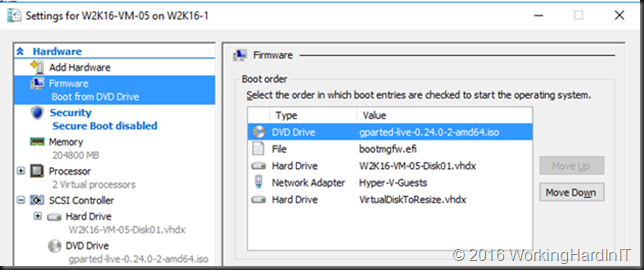
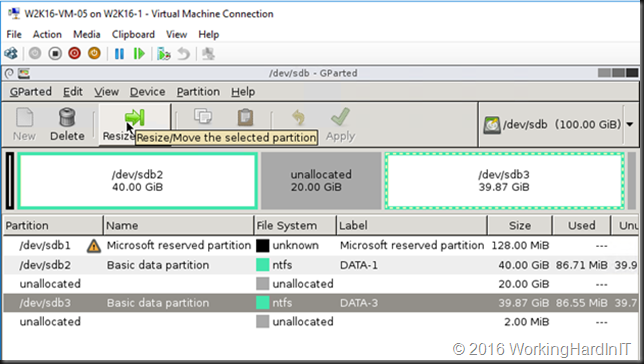
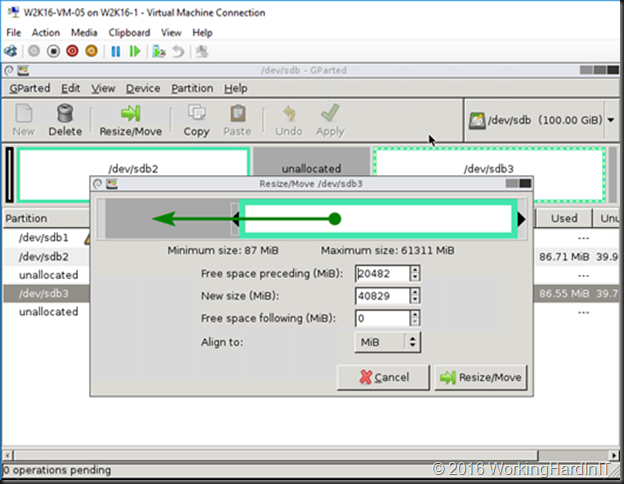
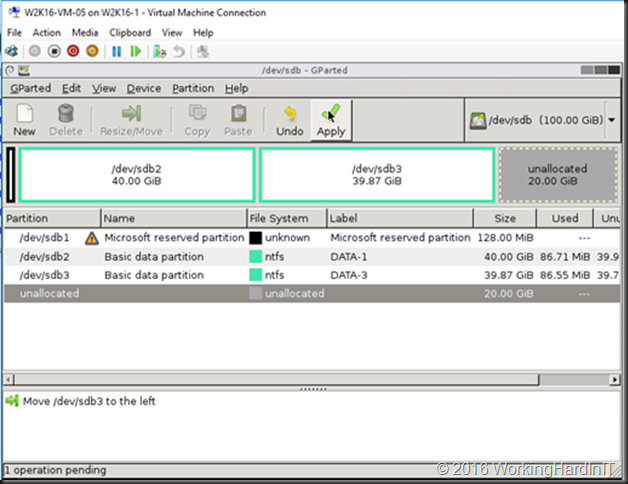
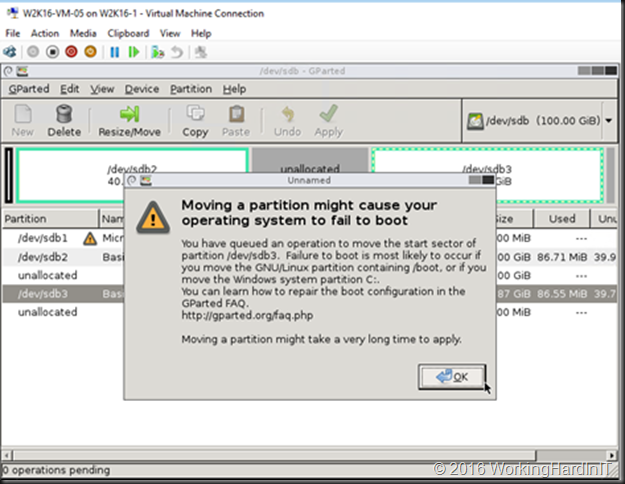
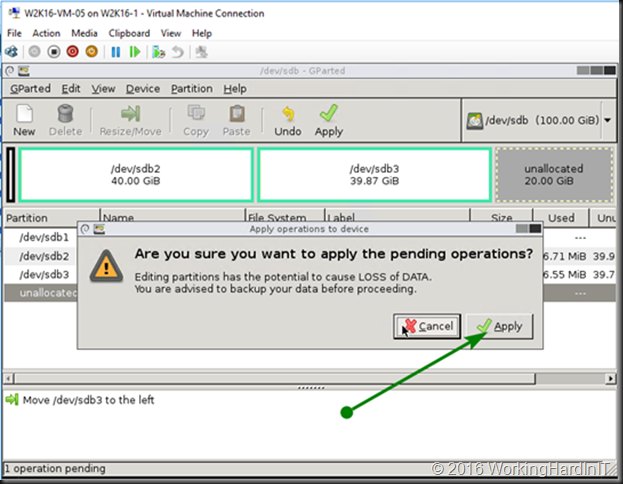
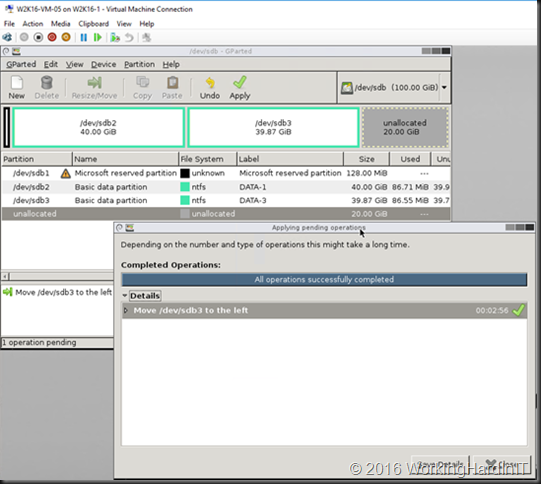
Unless you can delete volume volume H: and create it again to restore the data to the new volume which is then at the end of volume F: you’ll need to turn to 3rd party tools. Free open source tools like GParted will do the job nicely and I have used it extensively. I have a blog post on using it Using Gparted to fix virtual disk resizing issues. You still want a backup or a copy of your vhdx before doing anything like that, just in case.
The results
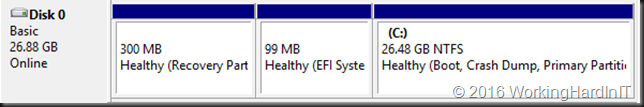
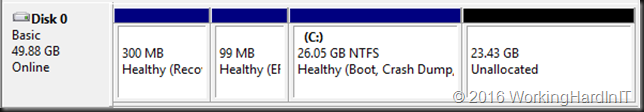
In the example above which is a lab setup, deleting the shadow copies and getting rid of the page file which was unfortunately located and prevent shrinking the volume more this allowed to shrink with 23GB instead of 11GB. Not bad.
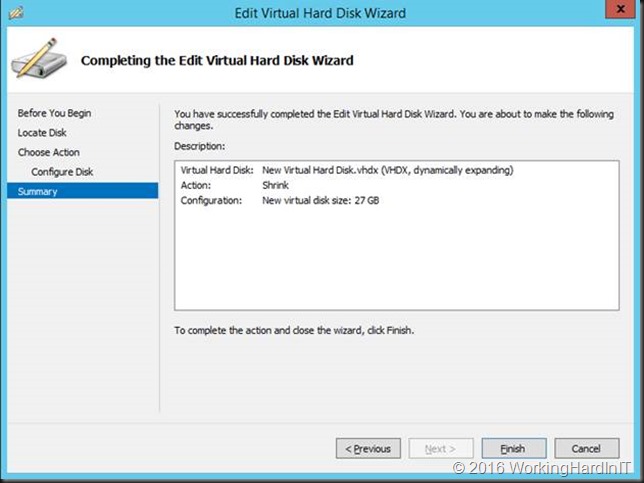
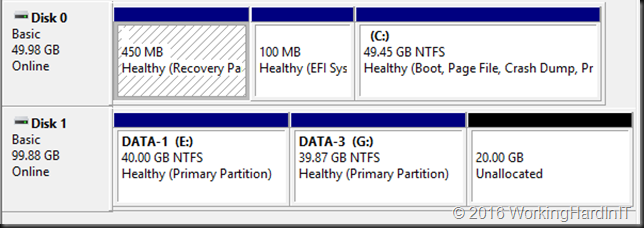
Which gives us 23GB of unallocated space on the virtual disk.
Which we can now shrink the virtual hard disk with that amount!
![clip_image013[1] clip_image013[1]](https://blog.workinghardinit.work/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/clip_image0131_thumb.png)
The little extra unallocated space left is taken care or by extending the disk a little. Done!
![clip_image014[1] clip_image014[1]](https://blog.workinghardinit.work/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/clip_image0141_thumb.png)
Don’t forget to turn the page file back on in the best possible configuration for your workload afterwards and re-enable shadow copies if needed.
A real Word Example
A real world example of this is when we needed to move a 120 GB of indexing files to a dedicated virtual disk because it was causing the OS volume, the C:\ drive to run out of space. We could and did not want to grow virtual hard disk on which the guest OS drive was located. After we had moved the index we wanted to shrink the volume with about 120 GB, leaving ample frees space for the OS volume to function optimally but we could not. We could gain a pitiful 2GB of space!
First we made sure the index data was shift deleted and ran the optimizer to defrag the disk but that did not help. We check for shadow copies but there were none present. As this was a virtual server we did not have a hyberfil.sys file to worry about. In the end what did the trick for us was disabling the page file, rebooting the virtual machines, shrinking the volume and rebooting the virtual machine again.
Conclusion
You have seen how to address an issue where, despite having free space in a volume you cannot shrink it, and as a result, cannot shrink a VHDX file in size. That was blocking our real goal here, which was to shrink the virtual hard disk. While the latter is possible on line we cannot always mitigate the issues we encounter with shrinking a volume (by itself an online event) without down time. Disabling or enabling the page file require a reboot. Defragmentation can be done on line most of the time, but not when it comes to NTFS metadata. Disabling and enabling shadow copies is an online process however.
This is of cause a prime example of what DevOps and cloud computing at scale is discouraging. That brave new world promotes threating your servers as cattle. When one is giving you an issue you don’t nurse it back to health but fire up the barbeque as Jeffrey Snover would put it. That’s a great model if it applies to your environment. But before you do so I’d make sure that your server is not a holy cow instead of cattle. For many applications, even modern ones, in the enterprise you cannot not just kill them off. If you do you’d better have great backups but even those will not solve issues like we one, we’ve addressed here. The backups are there to protect you when things go wrong with your interventions.

















![clip_image013[1] clip_image013[1]](https://blog.workinghardinit.work/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/clip_image0131_thumb.png)
![clip_image014[1] clip_image014[1]](https://blog.workinghardinit.work/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/clip_image0141_thumb.png)