Introduction
Below is a script that I use to collect cluster nodes with HBA WWN info. It grabs the cluster nodes and their HBA (virtual ports) WWN information form an existing cluster. In this example the nodes have Fibre Channel (FC) HBAs. It works equally well for iSCSI HBA or other cards. You can use the collected info in real time. As an example I also demonstrate writing and reading the info to and from a CSV.
This script comes in handy when you are replacing the storage arrays. You’ll need that info to do the FC zoning for example. And to create the cluster en server object with the correct HBA on the new storage arrays if it allows for automation. As a Hyper-V cluster admin you can grab all that info from your cluster nodes without the need to have access to the SAN or FC fabrics. You can use it yourself and hand it over to those handling them, who can use if to cross check the info they see on the switch or the old storage arrays.
Script to collect cluster nodes with HBA WWN info
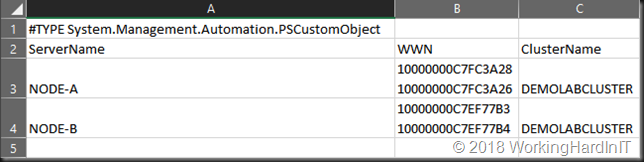
The script demos a single cluster but you could use it for many. It collects the cluster name, the cluster nodes and their Emulex HBAs. It writes that information to a CSV files you can read easily in an editor or Excel.
The scripts demonstrates reading that CSV file and parsing the info. That info can be used in PowerShell to script the creation of the cluster and server objects on your SAN and add the HBAs to the server objects. I recently used it to move a bunch of Hyper-V and File clusters to a new DELLEMC SC Series storage arrays. That has the DELL Storage PowerShell SDK. You might find it useful as an example and to to adapt for your own needs (iSCSI, brand, model of HBA etc.).
#region Supporting Functions
Function Convert-OutputForCSV {
<#
.SYNOPSIS
Provides a way to expand collections in an object property prior
to being sent to Export-Csv.
.DESCRIPTION
Provides a way to expand collections in an object property prior
to being sent to Export-Csv. This helps to avoid the object type
from being shown such as system.object[] in a spreadsheet.
.PARAMETER InputObject
The object that will be sent to Export-Csv
.PARAMETER OutPropertyType
This determines whether the property that has the collection will be
shown in the CSV as a comma delimmited string or as a stacked string.
Possible values:
Stack
Comma
Default value is: Stack
.NOTES
Name: Convert-OutputForCSV
Author: Boe Prox
Created: 24 Jan 2014
Version History:
1.1 - 02 Feb 2014
-Removed OutputOrder parameter as it is no longer needed; inputobject order is now respected
in the output object
1.0 - 24 Jan 2014
-Initial Creation
.EXAMPLE
$Output = 'PSComputername','IPAddress','DNSServerSearchOrder'
Get-WMIObject -Class Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration -Filter "IPEnabled='True'" |
Select-Object $Output | Convert-OutputForCSV |
Export-Csv -NoTypeInformation -Path NIC.csv
Description
-----------
Using a predefined set of properties to display ($Output), data is collected from the
Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration class and then passed to the Convert-OutputForCSV
funtion which expands any property with a collection so it can be read properly prior
to being sent to Export-Csv. Properties that had a collection will be viewed as a stack
in the spreadsheet.
#>
#Requires -Version 3.0
[cmdletbinding()]
Param (
[parameter(ValueFromPipeline)]
[psobject]$InputObject,
[parameter()]
[ValidateSet('Stack', 'Comma')]
[string]$OutputPropertyType = 'Stack'
)
Begin {
$PSBoundParameters.GetEnumerator() | ForEach {
Write-Verbose "$($_)"
}
$FirstRun = $True
}
Process {
If ($FirstRun) {
$OutputOrder = $InputObject.psobject.properties.name
Write-Verbose "Output Order:`n $($OutputOrder -join ', ' )"
$FirstRun = $False
#Get properties to process
$Properties = Get-Member -InputObject $InputObject -MemberType *Property
#Get properties that hold a collection
$Properties_Collection = @(($Properties | Where-Object {
$_.Definition -match "Collection|\[\]"
}).Name)
#Get properties that do not hold a collection
$Properties_NoCollection = @(($Properties | Where-Object {
$_.Definition -notmatch "Collection|\[\]"
}).Name)
Write-Verbose "Properties Found that have collections:`n $(($Properties_Collection) -join ', ')"
Write-Verbose "Properties Found that have no collections:`n $(($Properties_NoCollection) -join ', ')"
}
$InputObject | ForEach {
$Line = $_
$stringBuilder = New-Object Text.StringBuilder
$Null = $stringBuilder.AppendLine("[pscustomobject] @{")
$OutputOrder | ForEach {
If ($OutputPropertyType -eq 'Stack') {
$Null = $stringBuilder.AppendLine("`"$($_)`" = `"$(($line.$($_) | Out-String).Trim())`"")
}
ElseIf ($OutputPropertyType -eq "Comma") {
$Null = $stringBuilder.AppendLine("`"$($_)`" = `"$($line.$($_) -join ', ')`"")
}
}
$Null = $stringBuilder.AppendLine("}")
Invoke-Expression $stringBuilder.ToString()
}
}
End {}
}
function Get-WinOSHBAInfo {
<#
Basically add 3 nicely formated properties to the HBA info we get via WMI
These are the NodeWWW, the PortWWN and the FabricName. The raw attributes
from WMI are not readily consumable. WWNs are given with a ":" delimiter.
This can easiliy be replaced or removed depending on the need.
#>
param ($ComputerName = "localhost")
# Get HBA Information
$Port = Get-WmiObject -ComputerName $ComputerName -Class MSFC_FibrePortHBAAttributes -Namespace "root\WMI"
$HBAs = Get-WmiObject -ComputerName $ComputerName -Class MSFC_FCAdapterHBAAttributes -Namespace "root\WMI"
$HBAProperties = $HBAs | Get-Member -MemberType Property, AliasProperty | Select -ExpandProperty name | ? {$_ -notlike "__*"}
$HBAs = $HBAs | Select-Object $HBAProperties
$HBAs | % { $_.NodeWWN = ((($_.NodeWWN) | % {"{0:x2}" -f $_}) -join ":").ToUpper() }
ForEach ($HBA in $HBAs) {
# Get Port WWN
$PortWWN = (($Port |? { $_.instancename -eq $HBA.instancename }).attributes).PortWWN
$PortWWN = (($PortWWN | % {"{0:x2}" -f $_}) -join ":").ToUpper()
Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -InputObject $HBA -Name PortWWN -Value $PortWWN
# Get Fabric WWN
$FabricWWN = (($Port |? { $_.instancename -eq $HBA.instancename }).attributes).FabricName
$FabricWWN = (($FabricWWN | % {"{0:x2}" -f $_}) -join ":").ToUpper()
Add-Member -MemberType NoteProperty -InputObject $HBA -Name FabricWWN -Value $FabricWWN
# Output
$HBA
}
}
#endregion
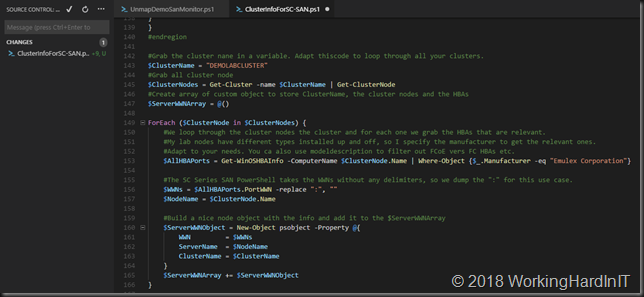
#Grab the cluster nane in a variable. Adapt thiscode to loop through all your clusters.
$ClusterName = "DEMOLABCLUSTER"
#Grab all cluster node
$ClusterNodes = Get-Cluster -name $ClusterName | Get-ClusterNode
#Create array of custom object to store ClusterName, the cluster nodes and the HBAs
$ServerWWNArray = @()
ForEach ($ClusterNode in $ClusterNodes) {
#We loop through the cluster nodes the cluster and for each one we grab the HBAs that are relevant.
#My lab nodes have different types installed up and off, so I specify the manufacturer to get the relevant ones.
#Adapt to your needs. You ca also use modeldescription to filter out FCoE vers FC HBAs etc.
$AllHBAPorts = Get-WinOSHBAInfo -ComputerName $ClusterNode.Name | Where-Object {$_.Manufacturer -eq "Emulex Corporation"}
#The SC Series SAN PowerShell takes the WWNs without any delimiters, so we dump the ":" for this use case.
$WWNs = $AllHBAPorts.PortWWN -replace ":", ""
$NodeName = $ClusterNode.Name
#Build a nice node object with the info and add it to the $ServerWWNArray
$ServerWWNObject = New-Object psobject -Property @{
WWN = $WWNs
ServerName = $NodeName
ClusterName = $ClusterName
}
$ServerWWNArray += $ServerWWNObject
}
#Show our array
$ServerWWNArray
#just a demo to list what's in the array
ForEach ($ServerNode in $ServerWWNArray) {
$Servernode.ServerName
ForEach ($WWN in $Servernode.WWN)
{$WWN}
}
#Show the results
$Export = $ServerWWNArray | Convert-OutputForCSV
#region write to CSV and read from CSV
#You can dump this in a file
$Export | export-csv -Path "c:\SysAdmin\$ClusterName.csv" -Delimiter ";"
#and get it back from a file
Get-Content -Path "c:\SysAdmin\$ClusterName.csv"
$ClusterInfoFile = Import-CSV -Path "c:\SysAdmin\$ClusterName.csv" -Delimiter ";"
$ClusterInfoFile | Format-List
#just a demo to list what's in the array
$MyClusterName = $ClusterInfoFile.clustername | get-unique
$MyClusterName
ForEach ($ClusterNode in $ClusterInfoFile) {
$ClusterNode.ServerName
ForEach ($WWN in $ClusterNode.WWN) {
$WWN
}
}