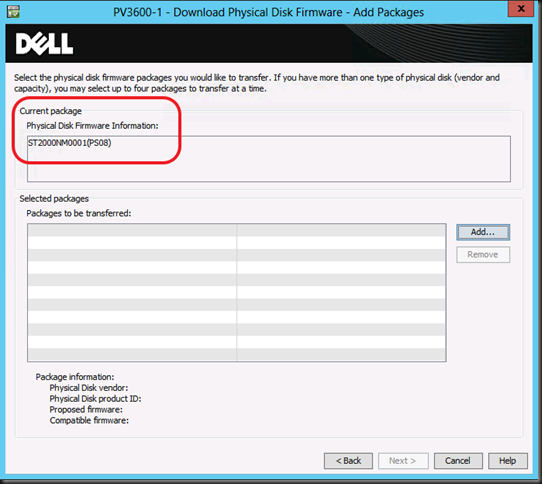
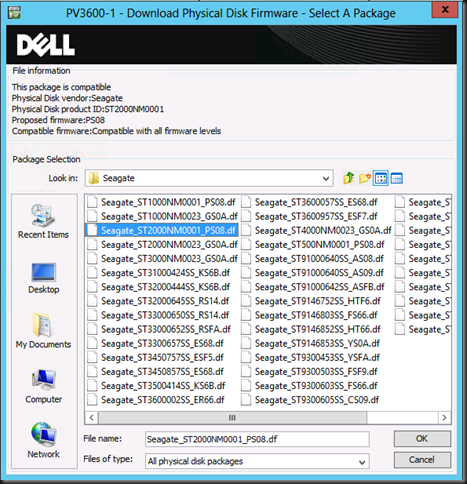
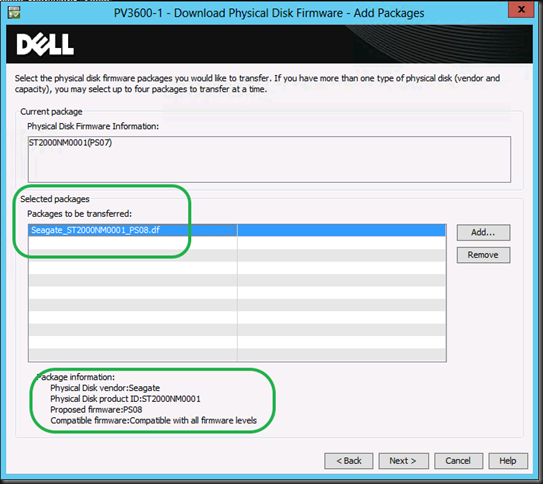
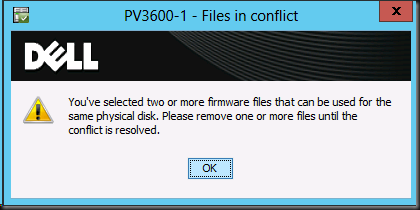
Pointy Haired Managers
Time for an entry in The Dilbert® Life series, which are post on corporate culture from hell and dysfunctional organizations running wild. This can be quite shocking and sobering to those who take themselves to serious. So these blog posts need to be read with a healthy dose of humor and be put into perspective. If you can’t do that, leave now.
I see my part of corporate bullshit & a total lack of real insight, let alone vision. To be fair, the amount of crap managers gets to see from their employees is also considerable ![]() as you can read here. I do not expect all managers to be a genuine leaders, that would be overly ambitious of me. But some common sense might come in handy. Every now and then, when some managers feel the need to make a name for themselves, an entire process tends to repeat it self. Part of that is the need to improve things and services in ways that have no real value & only seem to have a cost. The good news about this is that responding to this is very economical as you can just reuse all your previous e-mails & notes debunking it. Their game plan for the above is never ever original, but sometimes it does contain a secondary agenda.
as you can read here. I do not expect all managers to be a genuine leaders, that would be overly ambitious of me. But some common sense might come in handy. Every now and then, when some managers feel the need to make a name for themselves, an entire process tends to repeat it self. Part of that is the need to improve things and services in ways that have no real value & only seem to have a cost. The good news about this is that responding to this is very economical as you can just reuse all your previous e-mails & notes debunking it. Their game plan for the above is never ever original, but sometimes it does contain a secondary agenda.
Command & Control
First thing that always pops up is the old & long wish list of making pigs fly as requested by other middle managers, i.e. their peers This caters to the needs to be perceived as “being able to get it done”. This is also a drag but it isn’t difficult to deal with either. It’s like singing the same song over and over again, but heck we know the tune & the words by hard.
The second thing is planning. Schedules, vacation, capacity planning, resource allocations. It’s the need to assert control or at least the illusion. Be in charge of the sheep. This is a double edged sword as flexibility works both ways. What you take away form employees, you lose too! While some managers are ridiculously blunt at it, some show more finesse but in the end it aids in showing some “executive power” to their peers as well, as they got a grip on the ‘IT Crowd’ who are seen like I described before in The do’s and don’ts when engaging consultants Part II:
“Well those IT people are a tough crowd. They are opinionated and don’t communicate to well. Hell those guys & gals prefer to work with machines! They are not up to speed with what is politically correct or fashionable, hate faking, can’t stand save asses and don’t tolerate kiss asses. Good IT people live by the sword and die by the sword. It’s all very direct. Either their solution works or it doesn’t. You can’t hide behind reports, gold plated words or lies when you work in IT. The evidence is there every single second of every single day, staring you right in the face. So basically it’s no wonder that weak management and incompetent employees can’t get along with them very well, they are a bit too direct.”
That’s all fine. But I prefer leaders over managers, as one manages resources, not people. In that respect I consider the term “Human Resources” a huge mistake. I prefer to work at places where I get the freedom & flexibility to produce great results. If they can’t offer that, things tend to become mediocre, their choice. Control works both ways and the more control you exert, the less flexible employees become as the race to the bottom sets in while your best “opt out”. Not that I have any illusion of being important, but I digress ![]() .
.
If it works for the business and that’s where they make the money & profit, well done, who am I to argue? What isn’t fine however is when middle management only talks the talk but never walks the walk in regards to being on call, standby, whatever you want to call it. If done professionally, well organized, with insight and purpose it’s perfectly fine and acceptable on a voluntary and compensated basis. You know, the kind of job where you know what you get into. However, often the services aren’t well defined, let alone that is known what is needed to support them and if that is even feasible. But they bring up that subject as every now and then, some of the talking heads get off on buzz words like SLAs, 24/7 economy, etc. It must be the self aggrandizing thrill of being in control of mission critical systems I guess. All that while knowing that often the one and only really time critical & very specialized app has been running on the dedication & voluntarism of exactly one guy for the past decade at that place (I kind of hope he wins the lottery). Please, unless you’ve got you purposely designed application running as SAAS on Amazon/Azure in different global regions or on premise in 3 different locations you’re not really mission critical. That means you should not even consider trying to do this. The manufacturing industry can learn you something here. Pay good people good money to do well defined work in weekend/night shifts. Don’t combine this with normal hours, it’s a recipe for failure. It trying to reap the economic benefits of crisis efforts as a normal way of doing business.
Put Up or Shut Up
Basically that’s my answer to being on call but in an ever so diplomatic way. My and your time is limited. It’s truly something you can not recuperate, resurrect or create. It’s never ever coming back. So when I’m asked (or I some cases told) I need to be on stand by or on watch, then we must discuss terms & conditions. But first of all I remind them that if they don’t have their act together and have designed for 24/7 they will fail at achieving their goals.
What is my role?
- Architect
- Leader & Coach
- Advisor / Consultant
- Virtualization Expert
- Systems Engineer
- Storage Engineer
- Network Engineer
- Operational Employee
I can and I do combine many of these roles with great success. But one cannot do everything for everyone. Some skill sets come at a cost. You pay me to be a systems engineer and you’ll get a very good one. Just don’t expect me to throw in architecture & strategic advice for free. You are either willing to pay for that or you’re not. That is your prerogative, as it is mine not to accept an offer. But being on call isn’t in that list as a role. It’s a feature that comes at a (high) cost both in money and in time and it impacts my ability to perform certain roles full or part time. So unless you’re willing to pay top dollar, my diplomatic answer is that “I’m not available for the next 6 months”. I don’t do low ball rates. It’s the same as in consulting or jobs. I’d rather work 40 hours per week in a well paid interesting job with 6 weeks vacation instead of 60 hours first level support for low ball rates and 2 weeks off. But this answer won’t work when you’re already an employee. In that case you need t explain it a bit more.
If you’re not willing to pay, why would I?
Regarding being on call. You are limiting me in my free/spare time. Time when I’m not supposed to be working for you as I have already done my part (often more).
I can’t enjoy a glass of wine at a party or BBQ. I can’t go on a spontaneous day trip or weekend. I can’t work on another project or hobby. I need to stay in the neighborhood of a phone, laptop, internet connection and transport. Darn, perhaps I’ll even need to buy a car as currently in this digital age I don’t really need one. I can work very productively from anywhere in the world. But basically standby means I’m grounded. So if you want me to be on call in a weekend for 48 hours that is going to cost you money, time or a combination of both.
- My hourly rate, that’s what you pay for my skill sets. You’re buying my expertise and not only time. This rate reflects my value, not your willingness or capability to pay them. My rates are high. The good news is that you probably don’t need me.
- As I have to reserve my time exclusively to you during those specific hours (whether you need them or not is your risk, not mine) has to be compensated in time, money or both. That’s the cost of retaining me.
- The fact that those hours are also evenings and at night make them more premium as you have a serious impact on my other engagements & opportunities, both personal & professional. That’s extra again in either time, money or both.
- I get to bear increased responsibility and stress without any long-term reward. You just add this to my plate while you hope that I’ll keep shining in all roles mentioned above. But you’re undermine my capabilities to do so by being on call and you’d like me do some management on top of that to convince others in the team of this worthy cause.
- You limit my chances at promotions. You might not want to lose the person who does this.
- What you get for free or this cheap is rarely valued, so it’s a very bad investment for me.
- You are going to make me walk out on my loved ones, family, friends, etc. for
€ 5/hour. What kind of message does that send? Hey my bosses have a 24/7 mission critical system I need to go deal with raking in a whopping € 5/hour (don’t laugh). So I’m out of here! Really? Is that what you tell your wife & children? I actually love my family .
.
Why on earth would you even think I’d agree to this whilst you love a scheme where I’m not even being paid if nothing happens? And if something really critical happens that can’t wait and I work throughout the night for 10 hours the value of saving decades of work, half a billion in data and make sure there is job to come back to for hundreds of people is worth € 50? Really, I think it can wait till Monday morning my friend. And if it’s really a crisis and we were able to help we have always done so, through the nights, in weekends for free, voluntarily. That’s our commitment on record, where is yours? So no we’re not being assholes. But I resent the cheap ease with which some people want to take control of my non working hours. You see most people who want this don’t really need it and are not organized to run 24/7 mission critical operations. It’s a bolt on, on top of the 40+ hours (I wish) one puts in.
My time, my life & well being cannot be bought with ridiculous tokens of appreciation. I cannot produce or acquire time. It’s a fixed resource, and limited. Basically I don’t care whether you appreciate me or not in this particular case. If you want this effort from me we’ll need to discuss compensation in both time and money. Serious time to compensate being restricted at moments and serious money because your appreciation has never gotten me a raise, promotion or a discount at the grocery store or doctors office. You see, they only take money. I don’t get any kicks out of being a sucker who fell for this and the hot babes don’t fall for it either (that’s what I hear anyway). If you can’t afford that, you don’t need me, meaning you have other and better options. It’s that simple. Or you’ll need to realize your half baked 24/7 “mission critical” system isn’t up to it’s task and bleeding to death but you just can’t use me to stop the bleeding. I’m not a tampon but a “valued employee”. You are pretending to be mission critical and while I’m perfectly fine that you’re acting out your fantasies, I am not playing. I’m banking on the cloud and your monthly bill to help you realize what mission critical really costs which will mean you’ll decide that good enough is good enough or organize it properly.
Arrogant?
OK, so I do a full time day job and when it comes to studying, learning and being good at my job I’m above average. Now on top of that, let’s say that you want to pay me € 125 for staying on or around my home 2 weekends per month, and being on call 2 nights per week. Excluding holidays & vacation well call it € 1250/year. That’s a months pay extra for some. It is and that’s a hard reality. But it’s not during office hours, it’s added time & restrictions at low ball rates. That’s still nice you might say. If I only ever have to intervene a few times per month by clicking a few buttons and perhaps only have 2 real interventions per year totaling 16 hours per year. That might sound like an OK deal for some people and a manager (I’m assuming here that he really needs this). But that’s not what you want me for. You want me there because I can think on my feet, have serious skill sets and I’m your best hope of saving your business from disaster. And I have proven that by the way, numerous times. How much do you pay a real good consultant during regular office hours? Enough said. In reality every time stuff goes wrong who get’s an e-mail or phone call when decisions need to be made and executed? Who can‘t be reached in weekends when the shit hits the fan or has to be literally dragged away from their family? Right! Think twice before you call me arrogant. And most certainly do not use it as a reason why I should do it and be happy for the “opportunity”.
Am I an entitled piece of s* without any work ethic!?
Nice try. You just had to say this huh? Now you’re going to make my digress a whole lot. Look dude, before the industrialization of the world you had very limited career options which all came down to scraping a living day by day and dying by the truckload due to famine, disease & violence. Later on we got a slew of options which gradually became a better deal for “the working class”. After slavery we got “free” slaves in the factories & mines (Foxcon employees still have to get out of that stage) and after an equally industrialized slaughter of men during a couple of world wars we got the age of the baby boomers. They saw massive improvements to their quality of life thanks to unions & organized social/economic negotiations in an era when Communism was perceived a threat. Ah, that short time in history when social peace & a thriving middle class was worth something to big business and governments (literally money). They lived & died in the belief they got their fair share when they worked hard and they had a good work ethic. People were loyal to their companies, they got a pension, social security. Reciprocity. Life was good as long as you didn’t go crazy, or that’s the dream they sold you. But that’s not us anymore. That social peace and giving out a fair share isn’t worth that much anymore as it used to be to the powers that be. The current active generations (that would be us) are the ones with all rights, but much less work ethic. Entitlement? Perhaps, but politics & business lead by example so what do you expect? Mind you I did not say we work less, far from it. Some elderly people I know are appalled at the hours we really work versus what is says on paper and they don’t get the “always on” world. We have no prospects of things getting better. On the contrary, everything we have is under constant attack and it’s getting worse by the day. You might not realize it yet because it’s being buffered by social security & benefits in Europe. And while some might even get more incentives to work less instead of more the golden sixties are not coming back. While I’m a firm believer in a just & social, caring society, I’m afraid the way we use it to keep up appearances is not the correct answer to the threats by big money & power to the quality of our existence. But don’t worry about having to work until you’re 70. You won’t even be able to. The only end game here is you’ll get no or less pension. And if you take care of yourself and save for retirement they just steal it under your nose at 1.5% interest (do the math) or by downright confiscating it as a tax to save the EU or wherever it is you live. The wealth of the world is being transferred (it seldom disappears) in ever greater numbers to ever less people. Thanks to all the brilliant economic think tanks who “believe” they are doing science. But I indeed digress and here ends the history lesson.
This was about me potentially being an entitled piece of s*. Well saying that to employees who have saved companies from annihilation at -14°C on a snowy winter night, at +35°C in summer, at nights, in the weekends, voluntarily, because he valued the business and the livelihood of people isn’t very nice. But perhaps that’s not enough and you’d like more for peanuts? That means that you’ll now even consider robbing me of the time I need to enjoy what I have while it lasts. Take a hike, thank you. On your way donate your peanuts to the monkeys in the zoo, that’s where they belong, not in your business. The economy is down but it’s not that bad. Not yet anyway.
We can agree to disagree, but don’t insult me
Both you and me are not obliged to do this. We both have the choice. If and when you can find the people & skill sets you need for peanuts I’ll say, good for you! But when the next question is, without missing a beat, when & where the external service provider or employees you’ve found willing to do this can reach me all times, I’ll politely but decisively disengage as this brings us back to the start of the discussion and I don’t want to waste time on going over all this again. Not even to mention the fact that I take such inconsiderate behavior as an insult.
Good News
My current CEO gets this. So, no, it’s not a real issue for me as an employee. I hope yours does to, if not walk away. You seldom lose valued employees, you lose them because you don’t, which means you don’t care and probably don’t need them anyway. While consulting, it’s “easier”, your rates will chase the riff raff away and if not you just say that you’re not available for the next 6 months.

![worthdemotivator[1] worthdemotivator[1]](https://blog.workinghardinit.work/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/worthdemotivator1_thumb1.jpg)
![economicsdemotivator[1] economicsdemotivator[1]](https://blog.workinghardinit.work/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/economicsdemotivator14_thumb.jpg)