So you upgraded your TS Gateway virtual machine on W2K8(R2) to RDS Gateway on W2K12(R2) too make sure you get the latest and the greatest functionality and cut off any signs of technology debt way in advance. Perhaps you were inspired by my blog series on how to do this, and maybe you jumped through the x86 to x64 bit hoop whilst at it. Well done.
Now when upgrading or migrating from W2K8(R2) a lot of people forget about some of the enhancements in W2K12(R2). This is especially true of you don’t notice much by doing so. That’s why I see people forget about UDP. Why? Well things will keep working as they did before Windows Server 2012 RDS Gateway over HTTP or over RPC-HTTP (legacy clients). I have seen deployments where both the Windows and the perimeter firewall rules to allow UDP over 3391 were missing. Let alone that UDP Transport over port 3391 was enabled in the transport settings. But then you miss out on the benefits it offers (an improved user experience over less than great network connections and with graphics) as well on those of that ever more capable thingy called RemoteFX, if you use that.
For you that don’t know yet: HTTP and UDP protocols are both used preferably by RD Gateway and are more efficient than RPC over HTTP which is better for scaling and experience under low bandwidth and bad connectivity conditions. When HTTP transport channels are up (in & outgoing traffic), two UDP side channels are set up that can be used to provide both reliable (RDP-UDP-R) and best-effort (RDP-UDP-L) delivery of data. UDP also leveraged SSL via the RD gateway because is uses Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS). For more info RD Gateway Capacity Planning in Windows Server 2012. Further more it proves you have no reason not to virtualize this workload and I concur!
So why not set it up!? So check you firewall rules on the RD Gateway Server and set the rules accordingly. Do the same for your perimeter firewalls or any other in between your users and your RD Gateway.
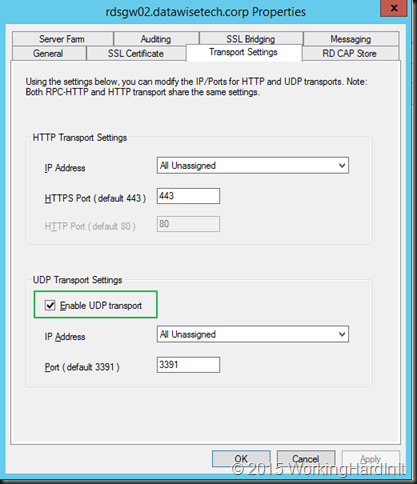
Under properties of your RS Gateway server you need to make sure UDP is enabled and listening on the needed IP address(es)
A client who connects over your RDS Gateway server, Windows Server 2012(R2) that is, and checks the network connection properties (click the “wireless NIC” like icon in the connection bar) sees the following: UDP is enabled. 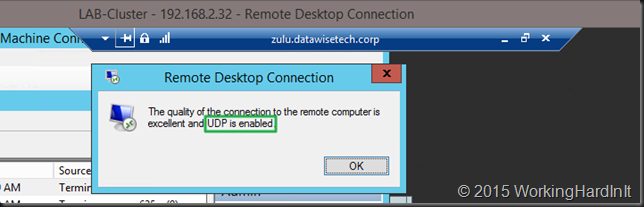 If they don’t see UDP as enabled and they aren’t running Windows 8 or 8.1 (or W2K12R2) they can upgrade to RDP 8.1 on windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2! When they connect to a Windows 7 SP1 or Windows 2008R2 machine make sure you read this blog post Get the best RDP 8.0 experience when connecting to Windows 7: What you need to know as it contains some great information on what you need to do to enable RDP 8/8.1 when connecting to Windows 7 SP1 or Windows 2008 R2:
If they don’t see UDP as enabled and they aren’t running Windows 8 or 8.1 (or W2K12R2) they can upgrade to RDP 8.1 on windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2! When they connect to a Windows 7 SP1 or Windows 2008R2 machine make sure you read this blog post Get the best RDP 8.0 experience when connecting to Windows 7: What you need to know as it contains some great information on what you need to do to enable RDP 8/8.1 when connecting to Windows 7 SP1 or Windows 2008 R2:
- “Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsRemote Desktop ServicesRemote Desktop Session HostRemote Session EnvironmentEnable Remote Desktop Protocol 8.0” should be set to “Enabled”
- “Computer ConfigurationAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsRemote Desktop ServicesRemote Desktop Session HostConnectionsSelect RDP Transport Protocols” should be set to “Use both UDP and TCP” => Important: After the above 2 policy settings have been configured, restart your computer.
- Allow port traffic: If you’re connecting directly to the Windows 7 system, make sure that traffic is allowed on TCP and UDP for port 3389. If you’re connecting via Remote Desktop Gateway, make sure you use RD Gateway in Windows Server 2012 and allow TCP port 443 and UDP port 3391 traffic to the gateway
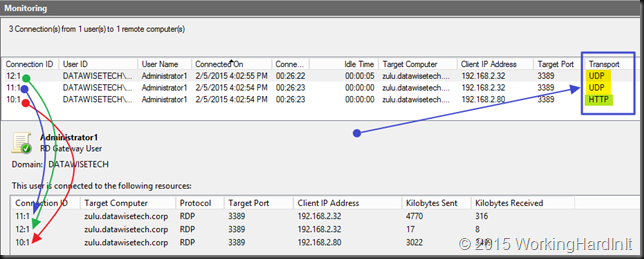
Cool you’ve done it and you verify it works. Under monitoring in the RD Gateway Manager you can see 3 connections per session: one is HTTP and the two others are UDP.
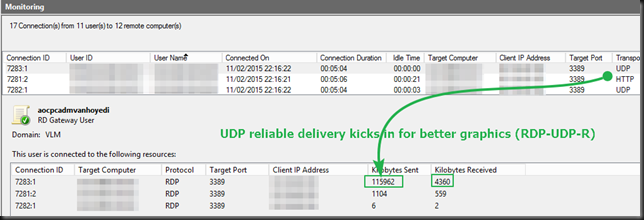
Life is good. But if you want to see the difference really well demonstrated try to connect to Windows 7 SP1 computer with RDP8 & TCP/UDP disabled and play a YouTube video, then to the same with RDP8 & TCP/UDP enabled, the difference is rather impressive. Likewise if you leverage RemoteFX in VM. The difference is very clear in experience, just try it! While you’re doing this look a the UDP “Kilobytes Sent” stats (refresh the monitoring tab, you’ll see UDP being put to work when playing a video on in your RDP session.