Introduction
There’s more to business continuity than having multiple locations. When it comes to high availability, or perhaps more accurately disaster recovery and business continuity people tend to focus on the good news. Some managers don’t want to be bothered by the details of our incompetency (i.e. reality and laws of physics) and vendors only like to focus on what they can sell with the biggest profit margin. Anything raining on that party falls under annoying details. When such a manager and such a sales man find each other it’s a match made in heaven. You’re the one who’s bringing the rain. It comes under the form of a simple question. How are we going to expose the failed over services internally and externally to the users and customers? What you mean that million-dollar investment in multiple SANs, clusters and consultants isn’t sufficient? Nope!
One piece of very good news is that in Windows Server 2016 Failover Clustering we can now leverage a cloud witness as well, next to a file share witness. This has the benefits we do not need a 3rd site for the file share witness. Which was not always feasible, sometimes a bit convoluted to achieve in the cloud via IAAS or depended on a rather less dependable server or PC somewhere in a branch office.
What’s the problem?
The problem is that failing over the workload with the services (VMs, SQL, File Servers, …) in a healthy, consistent state is only part of the challenge. The other part is to make sure that your clients (human or machines) can actually access those failed over services. If required or possible without noticing or with the smallest possible interruption possible. Even when you can achieve failover with only seconds of service interruption, some applications just can handle this gracefully or not at all.
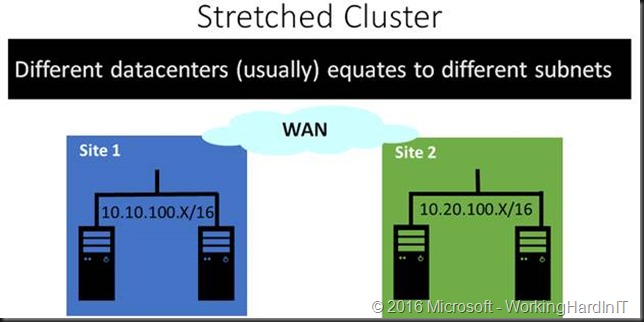
The thing is when you have multiple sites that often means distinct separate subnets / networks. So when that VM with IP address of 10.10.100.124 on default untagged VLAN 100 fails over to the other site how will the clients in the various branch offices or on the internet access it services? DNS point to 10.10.100.124 under normal conditions.
Well when the IP address can be updated for the DNS record thanks to “Multi-Subnet Resource Configuration” (SQL Server, File Share) thing will work again, eventually, given enough time.
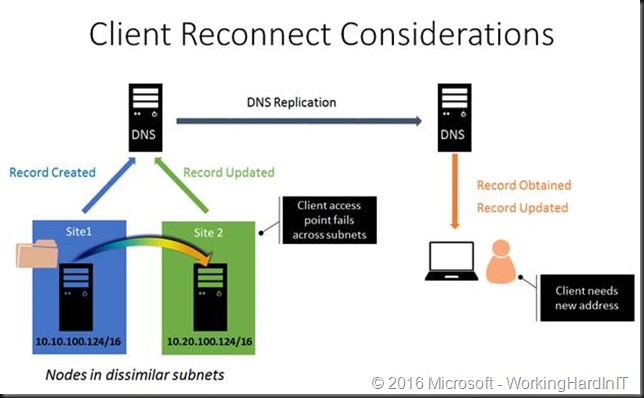
Multi-Subnet Resource Configuration works as follows. We have a single network name resource which we make dependent on multiple IP Address resources. In cluster terms that’s a “OR” decency when looking at the validation report. The secret sauce is that only one of the IP address resources of the network name resource is online at any given time. This gets registered in DNS and that’s what the clients use to access the service.
This works but the DNS record need to be upgraded, DNS replication needs to happen, client their DNS cache needs to expire and update etc. You can be looking at half an hour of down time actually.
But what if Multi-Subnet Resource Configuration isn’t an option or we’re in a hurry? What are options and how well and fast do these work? That’s the point at which the storage vendor is already counting the profits, the PM states the job’s done and the boss has already decided the project is a success and the network guys have some questions about YOUR problems. Let’s discuss some of options to deal with accessing services after a site activation.
Note: Hyper-V replica has the ability inject an alternate IP address on failover but we’re talking about a stretched cluster here, where replication happens at the storage level, not at the application level (Hyper-V) for the virtual machines.
Software Defined Networking Aka Network Virtualization.
Using Hyper-V Network Virtualization (HNV) abstract VMs logical subnet boundaries. This gives each virtual network the illusion it is running as a physical network. The typical example for this is multiple tenants that have the same IP space. The fact that it overlays physical network is also very handy when it comes to one and the same tenants in multi-site scenarios. Virtual networks allow VMs to move across different physical networks without re-configuring IP address in guest OS.
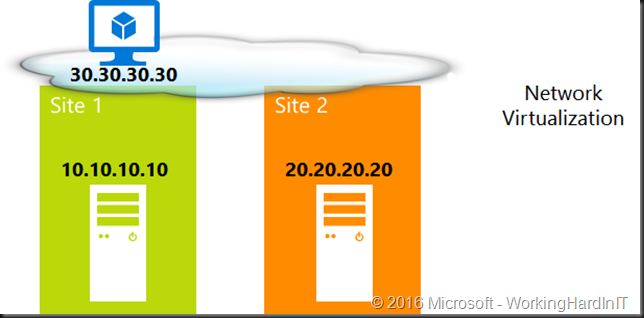
This totally abstracts the networks and it works great for virtual machines (Hyper-V). It doesn’t have to be limited to a single DC or site. Do note that there’s things to discuss around CSVs, Live Migration cluster wise and routing, gateways, DNS, geo load balancing access wise but you get the idea. When it comes to different subnets, different sites in regards to clustering things are not as easy as it seems. For this discussion we’re limiting ourselves to client connectivity to resources that move to another site and don’t dive into the details of network virtualization either.
Network Name Properties
There’s two cluster network name resource property setting you can configure to help reducing downtime after a failover.
RegisterAllProvidersIP cluster network name resource property
Remember our first story of “Multi-Subnet Resource Configuration” with the DNS updates and cache that has to expire? Well this can be enhanced as long as the applications can hand handle it. We can configure the DNS registration behavior via the RegisterAllProvidersIP property of a cluster networks name resource.
Get-ClusterResource MySQLServer |
Set-ClusterParameter RegisterAllProvidersIP 1
By setting this to TRUE all the IP address resources, on line and off line, are registered in DNS. If you have a “enlightened” application that can check for and handle multiple IP addresses and determine which one to use it allows for faster client reconnects. This works great with SQL Server.
HOstRecordTTL cluster network name resource property
This is great but has limited scope as the application has to have the logic to handle multiple registered IP addresses for the same resource and figure out when to use which one. SQL Server can do this, so can Exchange. What about a file server? RegisterAllProvidersIP won’t work but we can reduce the time to live of the DNS record for a cluster network resource IP address on the client from 20 minutes to 5 minutes or lower.
Get-ClusterResource MyFileShare |
Set-ClusterParameter HostRecordTTL 300
This is not an option for Hyper-V, there network virtualization works better or we use other options. Read on!
Stretch your VLANs
Here the VLAN(s) stretch across the sites. This means that the IP address of the service (VMs, SQL Servers, File Shares, …) never changes making it very easy to have the clients reconnect very fast.
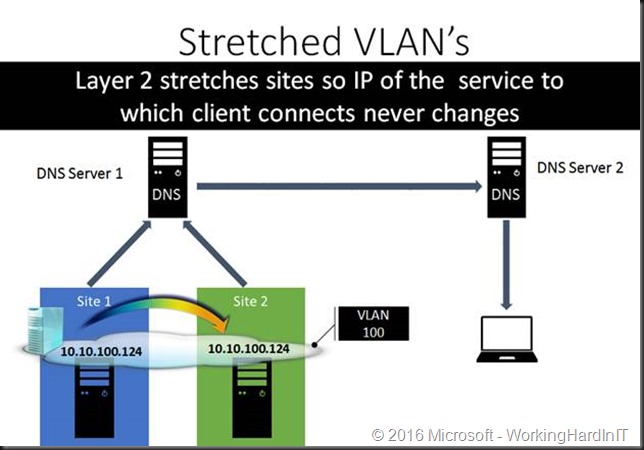
Easy for the apps and the system administrators. Well sort of, chances are that the networks admins will chip in and put a kill contract out on you with some assassins. Just saying. In a perfect world this would be a good idea. In reality layer 2 and spanning tree are making sure you’ll sort of regret it or at least deal with the drawback and fall out. Choose wisely.
Abstract the network devices
This is a network vendors provided solution and I don’t see it very much in the wild. In this approach the network devices use a 3rd IP address that get registered in DNS for use by the clients. The fact that the workload switches between subnets when failing over between sites is irrelevant to the clients.
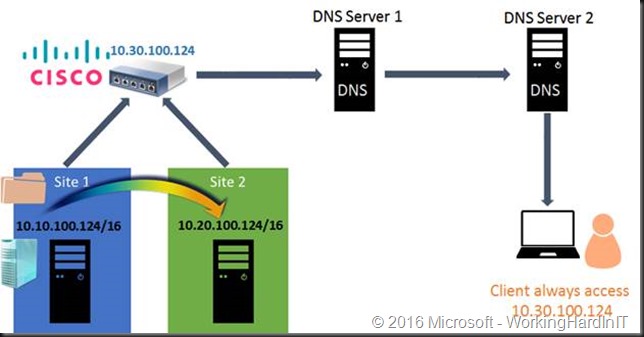
Cisco has this in a couple of solutions where NAT or a VIP is used to achieve this. As this is network appliance/ hardware based it works with any workload.
SLA your way out
Some people “mitigate” the prolonged down time by having a separate SLA for local failover versus site failover. Cool, but if I was cynical I could state that this is just lawyer behavior. You create fine print and “cover your ass” for that scenario. It’s not really solving anything but accepting longer down time and having all involved parties recognize and accept that fact. This is a valid approach.
Be creative & drive towards maximum portability
In an ideal world you can provision apps & services so fast you only need to protect and failover the persistent data. A world of micro services, containers where servers and virtual machines are cattle. But many of us will have to deal with servers being holey cows for now.
The above approaches are the most common options. There are more variations to these. One of those could be bases around the use of a dedicated management domain on both sites. It’s a concept I’ve used a couple of time where and when allowed.
It has some drawbacks or at least some complexities to deal with and one such example might be when configuring host based backups that need access to the guest VMs. This requires some extra firewall configuration. Nothing that would prevent you from doing so with good backup products like Veeam and it’s something you’re probably used to doing already for monitoring and backups across domains anyway.
But it also has serious benefits as the actual business domains are completely separate from the management domain and potentially 100% virtualized but that’s not a hard requirement as long as you keep the remaining physical servers in their own site dependent subnet which routes, these don’t move anyway, and they should have workloads that are distributed anyway like AD, Exchange DAGs, etc. The big benefits compared to a stretched cluster is that you can have the same subnet(s) on both sides of the stretched cluster for your virtual machines and you change the routing and endpoints for your public and private access to the services. Instead of making the changes to the cluster resources you do so higher up at the stack. It’s a bit like moving your data center to new location “as is” and directing the clients to the new location. This removes the need for stretched VLAN, or implementing network virtualization, at the cost of a bit more down time & work to “switch”. It’s worth considering.
It helps to leveraging DNS and geo load balancing technologies in this but the core infrastructure (the site ware stretched cluster) can run in a fully routed / Layer 3 fashion.
Sure you’ll still need to make sure the traffic from the offices goes to the correct data center now and it really rocks if you have your internet presence geo-load balanced in some way but let’s face it. But you needed to have that in order for any approach anyway.
Closing thoughts
There is a lot more detail and complexity to all of this than I covered in this short article. This is meant an eye opener, a point from where to start the discussion with the business demanding 24/7, 99.999% a zero cost and effort. Like Amazon or Azure but then better, cheaper and on premises. Ouch! As you might expect, this can’t be dealt with in just a few pages. Getting a solid, working disaster avoidance, recovery and business continuity plan & process is going to take some effort to create and maintain.
Fully failing over without any work or a second of downtime is a very expensive illusion and you might be better off with 15 to 20 minutes of down time for 90% of the workload and 30 to 60 minutes for the remaining 10% that trying to chase the ultimate perfection of 100% zero downtime ever for all services. Chances are you’ll go broke trying and pretending, which means failing. Remember that when your primary data center was just taken down or worse, burnt down, dealing with a couple of hours of down time to get you secondary site up and running 100 % isn’t actually as bad as it seems when discussing 2 or 3 hours of down time in a management meeting. Somehow it always seems a bigger deal when not faced with the alternative of the business being wiped out.
One final note, don’t forget to tell your bosses you’re going to have to practices this a couple of times per year. Doing it for real count’s a practice only if it’s the 3rd time you do it. Good luck!